3.3 SQL数据查询
3.3 SQL数据查询
3.3.1 SELECT命令的格式与基本使用
数据查询是数据库中最常见的操作。
SQL语言提供SELECT语句,通过查询操作可得到所需的信息。
SELECT语句的一般格式为:
1 | select〈列名〉[{,〈列名〉}] |
1 | select [all|distinct][top n [percent][with ties]] |
查询的结果是仍是一个表。
SELECT语句的执行过程是:
- 根据WHERE子句的检索条件,从FROM子句指定的基本表或视图中选取满足条件的元组,再按照SELECT子句中指定的列,投影得到结果表。
- 如果有GROUP子句,则将查询结果按照<列名1>相同的值进行分组。
- 如果GROUP子句后有HAVING短语,则只输出满足HAVING条件的元组。
- 如果有ORDER子句,查询结果还要按照<列名2>的值进行排序。
相关表格
S表
1 | use student |
1 | use student |
1 | use student |
1 | use student create table s |
1 | use student create table s ( |
1 | use student create table s ( |
1 | use student create table s ( |
1 | use student |
1 | use student |
1 | use student |
SC
1 | use student create table sc ( |
1 | use student create table sc ( |
1 | use student create table sc ( |
1 | use student |
1 | use student |
T表
1 | create cluster index ti on t(tn); |
1 | drop index sc.sci; |
例3.21 查询全体学生的学号、姓名和年龄。
1 | select sno, sn, age from s; |
例3.22 查询学生的全部信息。
1 | select * from s; |
用‘ * ’表示S表的全部列名,而不必逐一列出。
例3.23 查询选修了课程的学生号。
1 | select distinct sno from sc; |
查询结果中的重复行被去掉
投影查询
上述查询均为不使用WHERE子句的无条件查询,也称作投影查询。
另外,利用投影查询可控制列名的顺序,并可通过指定别名改变查询结果的列标题的名字。
例3.24 查询全体学生的姓名、学号和年龄。
1 | select sname name, sno, age from s; |
其中,name为sname的别名
3.3.2 条件查询
当要在表中找出满足某些条件的行时,则需使用WHERE子句指定查询条件。
WHERE子句中,条件通常通过三部分来描述:
1.列名;
2.比较运算符;
3.列名、常数
where子句常用的比较运算符
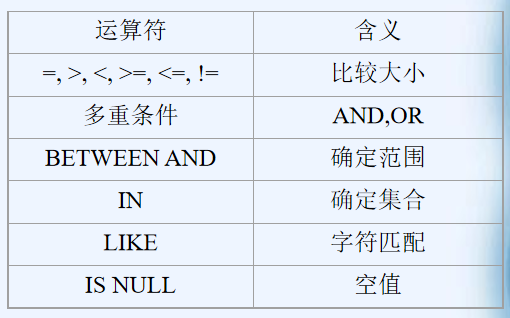
3.3.2.1 比较大小
1 | use student create table s ( |
1 | use student create table sc ( |
例3.25 查询选修课程号为‘C1’的学生的学号和成绩
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
展开/折叠
select sno,score from SC where cno='C1';
例3.26 查询成绩高于85分的学生的学号、课程号和成绩。
展开/折叠
select sno,cno,score from SC where score > 85;
3.3.2.2 多重条件查询
当where子句需要指定一个以上的查询条件时,则需要使用逻辑运算符and、or和not将其连结成复合的逻辑表达式。
其优先级由高到低为:not、and、or,用户可以使用括号改变优先级。
例3.27 查询选修C1或C2且分数大于等于85分学生的的学号、课程号和成绩。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
展开/折叠
select sno,cno,score from SC where (cno='C1' or cno = 'C2') and score >=85;
3.3.2.3 确定范围
例3.28 查询工资在1000至1500之间的教师的教师号、姓名及职称。
展开/折叠
select tno,tn,prof from T where sal>=1000 and sal <=1500;
例3.29 查询工资不在1000至1500之间的教师的教师号、姓名及职称。
展开/折叠
select tno,tn,prof from T where sal<1000 or sal>1500;
展开/折叠
select tno,tn,prof from t where sal not between 1000 and 1500 ;
3.2.2.4 确定集合
in
利用“in”操作可以查询属性值属于指定集合的元组。
例3.30 查询选修C1或C2的学生的学号、课程号和成绩。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
展开/折叠
select sno,cno,score
from SC
where cno in ('C1','C2');
此语句也可以使用逻辑运算符“OR”实现。
展开/折叠
select sno,cno,score from sc where cno='C1' or cno='C2';
not in
利用“not in”可以查询指定集合外的元组。
例3.31 查询没有选修C1,也没有选修C2的学生的学号、课程号和成绩。
展开/折叠
select sno,cno,score
from sc
where cno not in ('C1','C2');
等价于
展开/折叠
select sno,cno,score from sc where cno!='C1' and cno!='C2';
3.3.2.5 部分匹配查询
上例均属于完全匹配查询,当不知道完全精确的値时,用户还可以使用like或not like进行部分匹配查询(也称模糊查询)。
LIKE定义的一般格式为:
1 | <属性名> LIKE <字符串常量>; |
属性名必须为字符型,字符串常量的字符可以包含如下两个特殊符号:
%:表示任意知长度的字符串;_:表示任意单个字符。
例3.32 查询所有姓张的教师的教师号和姓名。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
展开/折叠
select tno,tn from T where tn like "张%";
例3.33 查询姓名中第二个汉字是“力”的教师号和姓名。
展开/折叠
selec tno,tn form t where tn like '__力%';
注:一个汉字占两个字符。
3.3.2.6 空值查询
某个字段没有值称之为具有空值(NULL)。
通常没有为一个列输入值时,该列的值就是空值。
空值不同于零和空格,它不占任何存储空间。
例如,某些学生选课后没有参加考试,有选课记录,但没有考试成绩,考试成绩为空值,这与参加考试,成绩为零分的不同。
例3.34 查询没有考试成绩的学生的学号和相应的课程号。
展开/折叠
select sno,cno from sc where score is null;
注意:这里的空值条件为IS NULL,不能写成SCORE=NULL。
3.2.2 常用库函数及统计汇总查询
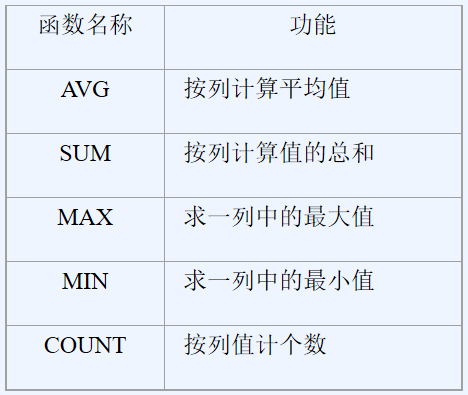
| 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| AVG | 按列计算平均值 |
| SUM | 按列计算值的总和 |
| MAX | 求一列中的最大值 |
| MIN | 求一列中的最小值 |
| COUNT | 按列值计个数 |
例3.35 求学号为S1学生的总分和平均分。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
展开/折叠
select sum(score) as totalScore,avg(score) as avgScore from SC where sno='S1';
注意:函数SUM和AVG只能对数值型字段进行计算。
例3.36 求选修C1号课程的最高分、最低分及之间相差的分数
展开/折叠
select max(score) as max_score,min(score) as min_score max(score)-min(score) as diff_score from sc where cno='C1';
例3.37 求计算机系学生的总数
展开/折叠
select count(sno) from s where dept='计算机';
例3.38 求学校中共有多少个系
展开/折叠
select count(distinct dept) as deptNum from s;
注意:加入关键字distinct后表示消去重复行,可计算字段“dept“不同值的数目。
count函数对空值不计算,但对零进行计算
例3.39 统计有成绩同学的人数
展开/折叠
select count(score) from sc;
上例中成绩为零的同学计算在内,没有成绩(即为空值)的不计算。
上面的写法中,凡是有成绩的学生都统计,如果一个学生选了多门课,并且他都去考试了,都有分数,那么将会有多个成绩。
这样的写法应该是有问题的,个人觉得应该改为如下的写法:
我还没验证,等验证之后再看
1 | select count(distinct sno) |
例3.40 利用特殊函数COUNT(*)求计算机系学生的总数
展开/折叠
select count(*) from s where dept='计算机';
count(*)用来统计元组的个数
不消除重复行,不允许使用distinct关键字。
如下写法是否可以
1 | select count(sno) |
3.3.3 分组查询
group by子句可以将查询结果按属性列或属性列组合在==行的方向上进行分组==,每组在属性列或属性列组合上==具有相同的值==。
例3.42 查询各位教师的教师号及其任课的门数。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
展开/折叠
select tno count(*) as c_num from tc group by tno;
group by子句按tno的值分组,所有具有相同tno的元组为一组,对每一组使用函数count进行计算,统计出各位教师任课的门数。
若在分组后还要按照一定的条件进行筛选,则需使用having子句。
例3.43 查询选修两门以上课程的学生学号和选课门数
展开/折叠
select sno,count(*) as sc_num from sc group by sno having count(*)>=2;
group by子句按sno的值分组,所有具有相同sno的元组为一组,对每一组使用函数count进行计算,统计出每位学生选课的门数。having子句去掉不满足count(*)>=2的组。
where子句group by和having子句的执行顺序
当在一个sql查询中同时使用where子句,group by 子句和having子句时,其顺序是where–>group by–> having。
where与having子句的根本区别在于作用对象不同。
where子句作用于基本表或视图,从中选择满足条件的元组;having子句作用于组,选择满足条件的组,必须用于group by子句之后,但group by子句可没有having子句。
3.3.5 查询的排序
- 当需要对查询结果排序时,应该使用
order by子句 order by子句必须出现在其他子句之后- 排序方式可以指定,
desc为降序,asc为升序,缺省时为升序
例3.44 查询选修C1 的学生学号和成绩,并按成绩降序排列。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
展开/折叠
selec sno,score from sc where cno='C1' order by score desc;
例3.45 查询选修C2、C3、C4,或C5课程的学号、课程号和成绩,查询结果按学号升序排列,学号相同再按成绩降序排列。
展开/折叠
select sno,cno,score
from sc
where (cno in ('C2','C3','C4')) or cno='C5'
order by sno asc,score desc;
例3.46 求选课在三门以上且各门课程均及格的学生的学号及其总成绩,查询结果按总成绩降序列出。
展开/折叠
select sno,sum(score) as total_score from sc where score>=60 group by sno having count(*)>=3 order by sum(score) desc;
分组排序执行过程
此语句为分组排序,执行过程如下:
1.(from)取出整个sc
2.(where)筛选score>=60的元组
3.(group by)将选出的元组按sno分组
4.(having)筛选选课三门以上的分组
5.(select)以剩下的组中提取学号和总成绩
6.(order by)将选取结果排序
简写
order by sum(score) desc可以改写成order by 2 desc2代表查询结果的第二列。
3.3.6 数据表连接及连接查询
- 数据表之间的联系是通过表的字段值来体现的,这种字段称为连接字段。
- 连接操作的目的就是通过加在连接字段的条件将多个表连接起来,以便从多个表中查询数据。
- 前面的查询都是针对一个表进行的,当查询同时涉及两个以上的表时,称为连接查询。
- 表的连接方法有两种:
- 方法1:表之间满足一定的条件的行进行连接,此时
from子句中指明进行连接的表名,where子句指明连接的列名及其连接条件。 - 方法2:利用关键字
join进行连接。
- 方法1:表之间满足一定的条件的行进行连接,此时
具体分为以下几种:
inner join:显示符合条件的记录,此为默认值;left(outer)join:显示符合条件的数据行,以及显示左边表中不符合条件的数据行,此时右边数据行会以null来显示,此称为左连接;right(outer)join:显示符合条件的数据行,以及右边表中不符合条件的数据行,此时左边数据行会以null来显示,此称为右连接;full(outer)join:显示符合条件的数据行,以及左边表和右边表中不符合条件的数据行,此时缺乏数据的数据行会以null来显示;cross join:会将一个表的每一笔数据和另一表的每笔数据匹配成新的数据行。
当将join关键词放于from子句中时,应有关键词on与之相对应,以表明连接的条件。
inner join(内连接)
内连接是一种一一映射关系,就是两张表都有的字段才能显示出来
用韦恩图表示是两个集合的交集,如图:
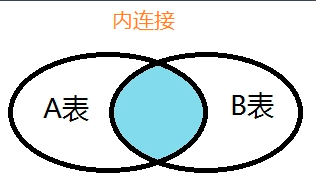
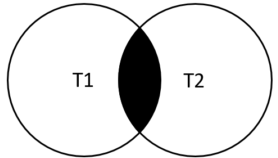
以下维恩图说明了INNER JOIN子句的工作原理。结果集中的行必须出现在两个表中:t1和t2,如两个圆的交叉部分所示:
https://www.yiibai.com/sql/sql-inner-join.html
https://www.runoob.com/sql/sql-join.html
左外连接
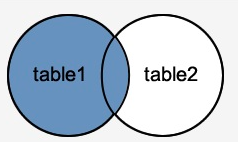
左连接将返回左表中的所有行,而不管右表中是否存在匹配的行。
假设有两个表A和B。表A有四行:1,2,3和4。表B还有四行:3,4,5,6。
当将表A与表B连接时,表A中的所有行(左表)都包含在结果集中,而不管无论表B中是否存在匹配的行。
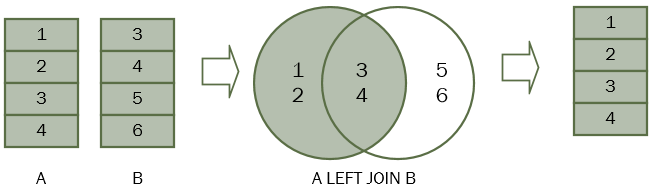
//原文出自【易百教程】,商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业请保留原文链接:https://www.yiibai.com/sql/sql-left-join.html
3.3.6.1 等值连接与非等值连接
例3.47 查询刘伟老师所讲授的课程。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
方法1:
展开/折叠
select t.tno,tn,cno from t tc where (t.tno=tc.tno)and tn='刘伟';
查询条件 连接条件 连接字段
这里,tn='刘伟'为查询条件,而t.tno = tc.tno为连接条件,tno为连接字段。连接条件的一般格式为:
1 | [<表名1>.] <列名1> <比较运算符> [<表名2>.] <列名2>; |
其中,比较运算符主要有:=、>、<、>=、<=、!=。
等值连接的定义
当比较运算符为“=“时,称为等值连接,其他情况为非等值连接。
引用列名tno时要加上表名前缀,是因为两个表中的列名相同,必须用表名前缀来确切说明所指列属于哪个表,以避免二义性。
如果列名是唯一的,比如tn,就不必须加前缀。
上面的操作是将t表中的tno 和tc表中的tno相等的行连接,同时选取tn为'刘伟'的行,然后再在tn,cno列上投影,这是连接、选取和投影的操作组合。
方法2:
1 | select t.tno,tn,cno |
方法3:
先尽量精简两张表的中的记录,然后再做连接操作
1 | select r2.tno,r2.tn, r1.cno |
例3.48 查询所有选课学生的学号、姓名、选课名称及成绩
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
先分析这些要查询的字段在那些表中:
1 | sno,--->S,SC |
可以看到涉及到三张表
这其中学生表S和课程表C是实体表,他们之间是多对多联系,SC表为联系表,所以可以使用SC表中的两个外键把S表和C表串联起来:
1 | select s.sno,s.sn,c.cn,sc.score |
本例涉及三个表,where子句中有两个连接条件。当有两个以上的表进行连接时,称为多表连接。
1 | select R1.sno,sn,cn,score |
3.3.6.2 自身连接
当一个表与其自已进行连接操作时,称为表的自身连接。
例3.49 查询所有比刘伟工资高的教师姓名、性别、工资和刘伟的工资。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
要查询的内容均在同一表T中,可以将表T分别取两个别名,一个是X,一个是Y。将X, Y 中满足比刘伟工资高的行连接起来。这实际上是同一表T的自身连接。
1 | select Y.tn,Y.sex,Y.sal,X.sal |
其他写法
展开/折叠
select Y.tn,Y.sex,Y.sal as sal_a,X.sal as sal_b
from
T as X
inner join
T as Y
on X.tn='刘伟' and Y.sal>X.sal;
1 | select Y.tn,Y.sex,Y.sal,X.sal |
1 | select R1.sn,R1.sex,R1.sal as sal_a,R2.sal as sal_b |
例3.50 检索所有学生姓名,年龄和选课名称。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
分析这些字段所在的表格:
1 | sn---S表 |
方法1
这需要三张表,三张表连接:
1 | select s.sn,s.age,c.cn |
方法2
1 | select R3.sno,R3.sn,R3.age,R4.cn |
或者:
1 | select R3.sn,R3.age c.cn |
3.3.6.3 外连接
在上面的连接操作中,不满足连接条件的元组不能作为查询结果输出。
如例3.48的查询结果只包括有选课记录的学生,而不会有吴丽同学的信息。若将例3.48改成:
例3.51 查询所有学生的学号、姓名、选课名称及成绩。(没有选课的同学的选课信息显示为空)则应写成如下的SQL语句
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
字段所在的表:
1 | sno sn--S |
1 | select s.sno,sn,cn,score |
则查询结果包括所有的学生,没有选课的吴丽同学的选课信息显示为空。
S left outer join SC效果:
| 字段名 | sno | sn | age | sex | dept | sno | cno | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 字段所在的表 | S | S | S | S | S | SC | SC | SC |
| 字段所在的表 | 非空 | 非空 | 非空 | 非空 | 非空 | 连接条件 | 可以为空 | 可以为空 |
SC left outer join C效果
| 字段名 | sno | cno | score | cn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 字段所在的表 | SC的字段 | SC的字段,C的字段,连接字段 | SC的字段 | C独有的字段,可以为NULL |
3.3.7 子查询
在where子句中包含一个形如select-from-where的查询块,此查询块称为子查询或嵌套查询,包含子查询的语句称为父查询或外部查询。
嵌套查询可以将一系列简单查询构成复杂查询,增强查询能力。
子查询的嵌套层次最多可达到255层,以层层嵌套的方式构造查询充分体现了SQL“结构化”的特点。
嵌套查询在执行时==由里向外==处理,每个子查询是在上一级外部查询处理之前完成,父查询要用到子查询的结果。
3.3.7.1 返回一个值的子查询
当子查询的返回值只有一个时,可以使用比较运算符=, >, <, >=, <=, !=将父查询和子查询连接起来。
例3.52 查询与刘伟教师职称相同的教师号、姓名。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
tno,tn–T,条件prof==刘伟的prof
—->先查询出刘伟的prof,tn=’刘伟’
1 | select tno,tn from T where prof=( |
此查询相当于分成两个查询块来执行。先执行子查询:
1 | select prof |
子查询向主查询只返回一个值,即刘伟教师的职称“讲师”,然后以此作为父查询的条件,相当于再执行父查询, 查询所有职称为“讲师”的教师号、姓名。
1 | select tno,tn |
1 | select tno,tn from T where T.prof |
3.3.7.2 返回一组值的子查询
如果子查询的返回值不止一个,而是一个集合时,则不能直接使用比较运算符,可以在比较运算符和子查询之间插入ANY或ALL。其具体含义详见以下各例。
1.使用ANY
例3.53 查询讲授课程号为C5的教师姓名。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
1 | select tn |
先执行子查询,找到讲授课程号为C5的教师号,为一组值构成的集合(T2,T3,T5);
再执行父查询,其中ANY的含义为任意一个,查询教师号为T2、T3、T5的教师的姓名。
该例也可以使用前面所讲的连接操作来实现:
tn—-T表
cno—TC
1 | select tn |
1 | select tn |
可见,对于同一查询可使用子查询和连接两种方法来解决,可根据习惯任意选用。
例3.54 查询其他系中比计算机系某一教师工资高的教师的姓名和工资。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
1 | select tn,sal from T |
- 先执行子查询,找到计算机系中所有教师的工资集合(1500,900);
- 再执行父查询,查询所有不是计算机系且工资高于1500或900的教师姓名和工资。
此查询也可以写成:
1 | select tn,sal from T |
- 先执行子查询,利用库函数
min找到计算机系中所有教师的最低工资——900; - 再执行父查询,查询所有不是计算机系且工资高于900的教师。
1 | select tn,sal from |
2. 使用IN
可以使用IN代替“=ANY”。
例3.55(题目同3.53)查询讲授课程号为C5的教师姓名。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
1 | select tn from T |
3. 使用ALL
ALL的含义为全部。
例3.56 查询其他系中比计算机系所有教师工资都高的教师的姓名和工资。
1 | select tn,sal from T |
- 子查询找到计算机系中所有教师的工资集合(1500,900);
- 父查询找到所有不是计算机系且工资高于1500的教师姓名和工资。
使用库函数max实现
此查询也可以写成:
1 | select tn,sal from T |
库函数max的作用是找到计算机系中所有教师的最高工资1500。
例3.57 查询不讲授课程号为C5的教师姓名。
1 | S(sno,sn,age,sex,dept) |
课程号cno—TC表
教师姓名tn—T表
1 | select distinct tn |
!=ALL的含义为不等于子查询结果中的任何一个值,也可使用NOT IN代替!=ALL。
相关子查询
子查询包含普通子查询和相关子查询。
前面所讲的子查询均为普通子查询,而本例中子查询的查询条件引用了父查询表中的属性值(T表的TNO值),我们把这类查询称为相关子查询