2021年09月24日 java1
考点1:垃圾回收机制
1 | static String str0="0123456789"; |
假定str0,…,str4后序代码都是只读引用。
Java 7中,以上述代码为基础,在发生过一次FullGC后,上述代码在Heap空间(不包括PermGen)保留的字符数为()
- A 5
- B 10
- C 15
- D 20
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: C常量池是PermGen的
这是一个关于java的垃圾回收机制的题目。垃圾回收主要针对的是堆区的回收,因为栈区的内存是随着线程而释放的。
堆区分为三个区:
年轻代(Young Generation)、
年老代(Old Generation)、
永久代(Permanent Generation,也就是方法区)。
年轻代:对象被创建时(new)的对象通常被放在Young(除了一些占据内存比较大的对象),经过一定的Minor GC(针对年轻代的内存回收)还活着的对象会被移动到年老代(一些具体的移动细节省略)。
年老代:就是上述年轻代移动过来的和一些比较大的对象。Minor GC(FullGC)是针对年老代的回收
永久代:存储的是final常量,static变量,常量池。
str3,str4都是直接new的对象,而substring的源代码其实也是new一个string对象返回。:
1 | public String substring(int beginIndex) { |
经过fullgc之后,年老区的内存回收,则年轻区的占了15个,不算PermGen。所以答案选C
考点2:递归
下面这段程序的输出结果是()
1 | public class Main { |
- A 12136
- B 63121
- C 61213
- D 11236
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: A这种题目还考眼力,代码不规范,格式化后的代码如下:
1 | public static int split(int number) { |
split(12);
12>1,true,进入外层if
12%2!=0,false,不进入内层if.
执行System.out.print(split(12 / 2));也就是System.out.print(split(6));
先执行split(6)
6>1,进入外层if
6 % 2 != 0,false,不进入内层if,执行System.out.print(split(6 / 2));也就是执行System.out.print(split(3));
先执行split(3)
3>1,true,进入外层if
3 % 2 != 0,true,进入内层if
执行System.out.print(split((3 + 1) / 2));也就是执行System.out.print(split(2));
先执行split(2)
2>1,true,进入外层if
2 % 2 != 0,false,不进入内层if
执行System.out.print(split(2 / 2));也就是执行System.out.print(split(1));先执行split(1)
1>1,false,不进入外层if,return 1,也就是split(1)=1执行System.out.print(split(1)),也就是System.out.print(1);,输出1,
执行sprint(2)的返回语句,返回2
执行System.out.print(split(2));也就是执行System.out.print(2);,输出2退出内层if
执行System.out.print(split(3 / 2));,也就是执行System.out.print(split(1));
先执行split(1)
1>1,false,不进入外层if,返回1,split(1)=1执行System.out.print(split(1));也就是执行执行System.out.print(1);,输出1
退出外层if,返回3,split(3)=3
执行System.out.print(split(3));也就是执行执行System.out.print(3);输出3
执行split(6)的返回语句,返回6,
执行System.out.print(split(6));也就是执行System.out.print(6);输出6
退出split(12)的外层if
split(12)返回12
考察方法进栈与出栈的顺序。先进后出
有个知识点,方法在出栈的时候,执行的是return语句。因为出栈就意味着方法结束并销毁,如果没有return语句,那么方法出栈的时候什么都不执行,就直接销毁。
1.执行split(12)时,执行代码System.out.print(split(number / 2))
split(12/2)进栈,此时number=6;
2.执行split(6)时,执行代码System.out.print(split(number / 2))
split(6/2)进栈,此时number=3;
3.执行split(3)时,
1 | 第1行 if (number % 2 != 0) |
按照顺序执行
先执行第2行
首先split((3+1)/2)进栈,此时number=2,
再执行split(2),那么split(2/2)进栈,此时number=1, 最后return 1,
注意此时第2行代码还没有结束
此时
split(2/2)出栈,输出1;
split((3+1)/2)出栈,输出2;
第二行代码结束,再执行第三行,此时number=3,执行System.out.print(split(number / 2))
split(3/2)进栈,number=1,return,那么就需要出栈了
split(3/2)出栈,输出1
split(6/2)出栈,输出3
split(12/2)出栈,输出6;
最终结果12136;
split(number)方法,最终返回的是number这个值,所以split(n)出栈的输出结果就是n
整理:
1 | split(12/2)进栈 |
考点3:JVM内存配置参数
对于JVM内存配置参数:
-Xmx10240m -Xms10240m -Xmn5120m -XXSurvivorRatio=3
,其最小内存值和Survivor区总大小分别是()
- A 5120m,1024m
- B 5120m,2048m
- C 10240m,1024m
- D 10240m,2048m
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: D| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| -Xmx: | 最大堆大小 |
| -Xms: | 初始堆大小 |
| -Xmn: | 年轻代大小 |
| -XXSurvivorRatio: | 年轻代中Eden区与Survivor的一个区的大小比值,Survivor有两个区 |
-Xms10240m,初始堆大小即最小内存值为10240m
-Xmn5120m,表示年轻代大小5120m
-XXSurvivorRatio=3表示Eden:S0:S1=3:1:1
Survivor区总大小=(5120/(3+1+1))*(1+1)=(5120/5)*2=1024*2=2048
考点4:Servlet ServletContext参数值
如何获取ServletContext设置的参数值?
- A context.getParameter()
- B context.getInitParameter()
- C context.getAttribute()
- D context.getRequestDispatcher()
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: BgetParameter()是获取POST/GET传递的参数值;
getInitParameter获取Tomcat的server.xml中设置Context的初始化参数
getAttribute()是获取对象容器中的数据值;
getRequestDispatcher是请求转发。
考点5:线程 InterruptedException
下面哪个行为被打断不会导致InterruptedException:( )?
- A Thread.join
- B Thread.sleep
- C Object.wait
- D CyclicBarrier.await
- E Thread.suspend
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: E抛InterruptedException的代表方法有:
java.lang.Object 类的 wait 方法
java.lang.Thread 类的 sleep 方法
java.lang.Thread 类的 join 方法
Thread只有sleep和join这两个方法抛出InterruptedException
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/lang/Thread.html
1 | public static void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException |
Thread的suspend方法
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/lang/Thread.html#suspend()
文档中描述如下
@Deprecated(since="1.2") public final void suspend()
Deprecated.
This method has been deprecated, as it is inherently deadlock-prone. If the target thread holds a lock on the monitor protecting a critical system resource when it is suspended, no thread can access this resource until the target thread is resumed. If the thread that would resume the target thread attempts to lock this monitor prior to calling resume, deadlock results. Such deadlocks typically manifest themselves as “frozen” processes. For more information, see Why are Thread.stop, Thread.suspend and Thread.resume Deprecated?.
Suspends this thread.
First, the checkAccess method of this thread is called with no arguments. This may result in throwing a SecurityException (in the current thread).
If the thread is alive, it is suspended and makes no further progress unless and until it is resumed.
Throws:
SecurityException - if the current thread cannot modify this thread.
See Also:
checkAccess()
没看到有抛出InterruptedException异常
Object类中只有wait方法抛出InterruptedException
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/lang/Object.html#wait()
1 | public final void wait() throws InterruptedException |
考点6:网路编程 URL类
URL u =new URL("http://www.123.com");。如果www.123.com不存在,则返回______。
- A
http://www.123.com - B
”” - C
null - D 抛出异常
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: Anew URL只检查URL的格式是否正确
new URL()时必须捕获检查异常,但这个异常是由于字符串格式和URL不符导致的,与网址是否存在无关。URL的toString方法返回字符串,无论网址是否存在。
示例
1 | public class URLtest { |
运行结果:
1 | http://www.agaeww123fjaoufoaufoajquroquroqj223453uuiu.com |
1 | public class URLtest { |
运行结果:
1 | java.net.MalformedURLException: no protocol: hello_world://www.nihao.com |
URL文档
public URL(String spec)
throws MalformedURLException
Creates a URL object from the String representation.
This constructor is equivalent to a call to the two-argument constructor with a null first argument.
Parameters:
spec - the String to parse as a URL.
Throws:MalformedURLException- if no protocol is specified, or an unknown protocol is found, or spec is null, or the parsed URL fails to comply with the specific syntax of the associated protocol.
See Also:
URL(java.net.URL, java.lang.String)
考点7:异常基础知识
下面哪些情况可以引发异常:
- A 数组越界
- B 指定URL不存在
- C 使用throw语句抛出
- D 使用throws语句
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: ABCthrows 和 throw:
throws出现在方法头,表示可能会出现异常;
throw是在方法体,抛出了异常,执行throw则一定抛出了某种异常
两者都是消极的异常处理方式,只是抛出或者可能抛出异常,是不会由函数处理,真正的处理异常由它的上层调用处理。
考点8:异常基础知识
下面有关 JAVA 异常类的描述,说法正确的有()
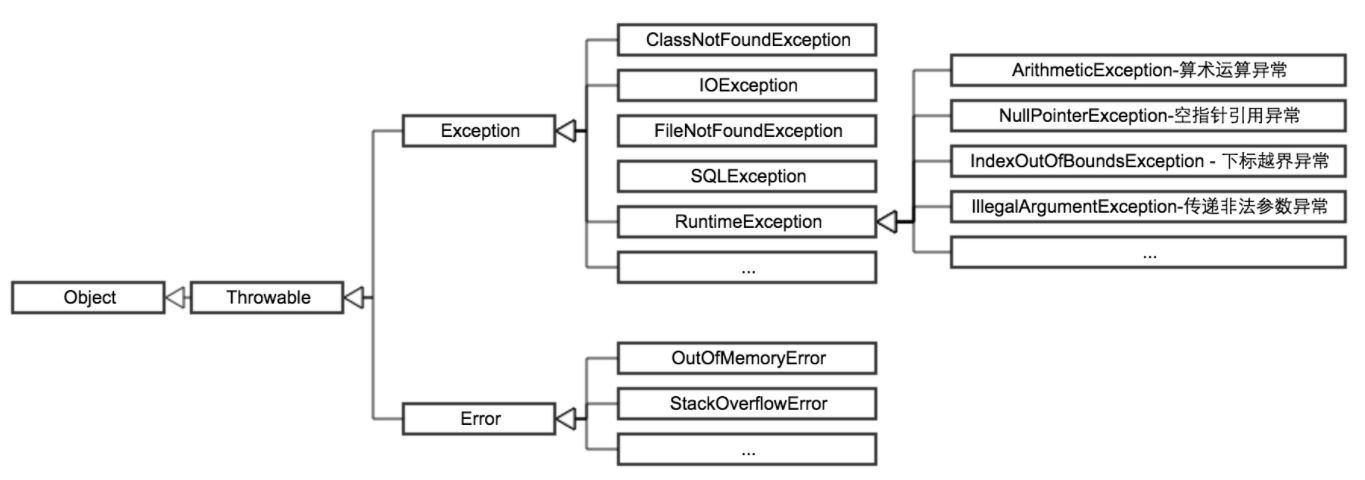
- A 异常的继承结构:基类为 Throwable,Error 和 Exception 。实现 Throwable, RuntimeException 和 IOException 等继承 Exception
- B 非 RuntimeException 一般是外部错误(不考虑Error的情况下),其可以在当前类被 try{}catch 语句块所捕获
- C Error 类体系描述了 Java 运行系统中的内部错误以及资源耗尽的情形,Error 不需要捕捉
- D RuntimeException 体系包括错误的类型转换、数组越界访问和试图访问空指针等等,必须 被 try{}catch 语句块所捕获
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: ABC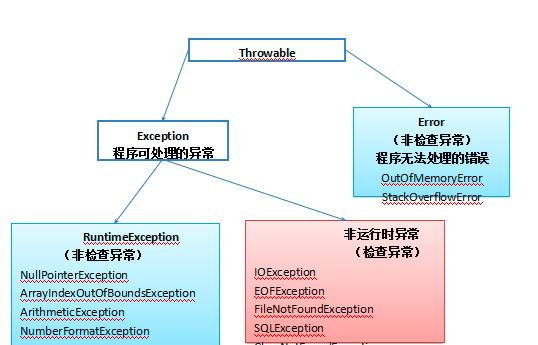
考点9:CMS垃圾收集器
CMS垃圾回收器在那些阶段是没用用户线程参与的
- A 初始标记
- B 并发标记
- C 重新标记
- D 并发清理
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: AC带并发的都是与用户线程一起执行的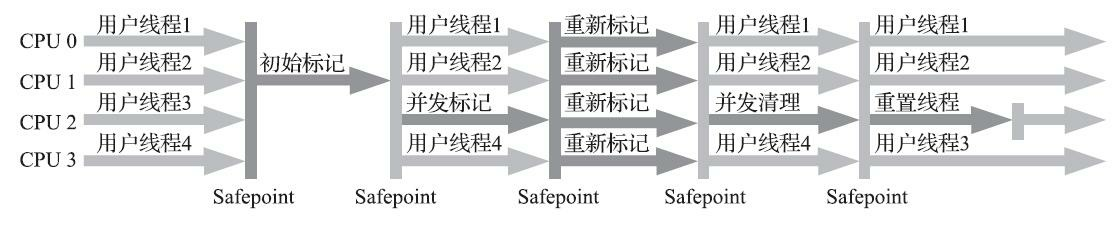
3.5.6 CMS收集器
考点10:线程基础知识
以下说法错误的是()
- A 其他选项均不正确
- B java线程类优先级相同
- C Thread和Runnable接口没有区别
- D 如果一个类继承了某个类,只能使用Runnable实现线程
显示答案/隐藏答案
正确答案: BCDThread和Runable有区别
Thread是一个类,Runable是一个接口。
Runable只有一个run方法,
而Thread除了有run方法,还有从Object继承来的方法,以及Thread中定义的start,sleep等方法。
1 | public class Thread |
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/lang/Thread.html#method.summary
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/11/docs/api/java.base/java/lang/Runnable.html#method.summary
实现线程的方式
- 继承Thread,然后调用Thread子类的start()方法启动线程
- 实现Runable接口,然后new Thread(new Runable实现类).start()
- 实现Callable接口,c=new Callable实现类,f=new FutureTask(c),new Thread(f).start()。然后通过f.get()获得线程的返回值。