第18章 基于注解的控制器
在第17章中,我们创建了两个采用传统风格控制器的Spring MVC应用程序,其控制器是实现了Controller接口的类。Spring 2.5版本引入了一个新途径:通过使用控制器注释类型。本章介绍了基于注解的控制器,以及各种对应用程序有用的注解类型。
18.1 SpringMVC注解类型
基于注解的控制器的优点
使用基于注解的控制器有几个优点。其一,一个控制器类可以处理多个动作(而一个实现了Controller接口的控制器只能处理一个动作)。这就允许将相关的操作写在同一个控制器类中,从而减少应用程序中类的数量。
其二,基于注解的控制器的请求映射不需要存储在配置文件中。使用RequestMapping注解类型,可以对一个方法进行请求处理。
Controller和RequestMapping注解类型是SpringMVC API最重要的两个注解类型。本章重点介绍这两个,并简要介绍了一些其他不太流行的注解类型。
18.1.1 Controller注解类型
org.springframework.stereotype.Controller注解类型用于指示Spring类的实例是一个控制器。下面是一个带注解@Controller的例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype;
...
@Controller
public class CustomerController {
}
|
Spring使用扫描机制来找到应用程序中所有基于注解的控制器类。为了保证Spring能找到你的控制器,需要完成两件事情。首先,需要在Spring MVC的配置文件中声明spring- context,如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
| <beans
...
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
...
>
|
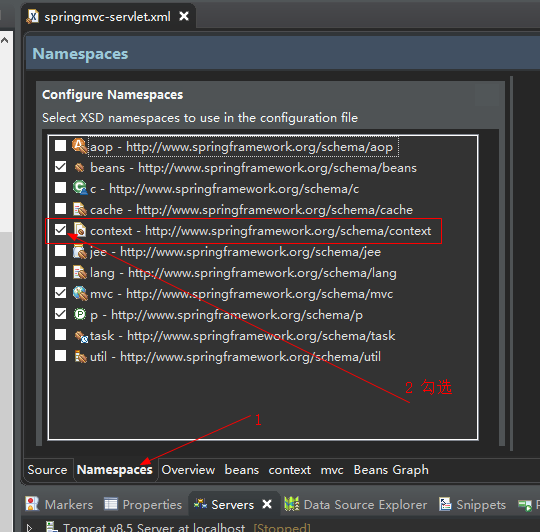
当然这个自己肯定是背不出来的,安装来Spring Toos3后可以点击文件下方的Namespaces标签,然后勾选上context即可:
![这里有一张图片]()
然后,需要应用<component-scan/>元素,如下所示:
1
| <context:component-scan base-package="basePackage"/>
|
请在<component-scan/>元素中指定控制器类的基本包。例如,若所有的控制器类都在com.example.controller及其子包下,则需要写一个如下所示的<component-scan/>元素:
1
| <context:component-scan base-package="com.example.controller"/>
|
现在,整个配置文件如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-
context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.controller"/>
</beans>
|
请确保所有控制器类都在基本包下,并且不要指定一个太广泛的基本包(例如不要指定大范围的com.example,而是指定小范围的com.example.controller),因为这会使得Spring MVC扫描了无关的包。
18.1.2 RequestMapping注解类型
现在,我们需要在控制类的内部为每一个动作开发相应的处理方法。要让Spring知道用哪一种方法来处理它的动作,需要使用org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping注释类型映射的URI与方法。
RequestMapping注解类型的作用就如同其名字所暗示的:映射一个请求和一种方法。可以使用@RequestMapping注解一种方法或类。
一个采用@RequestMapping注解的方法将成为一个请求处理方法,并由调度程序在接收到对应URL请求时调用。
下面是一个RequestMapping注解方法的控制器类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
...
@Controller
public class CustomerController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/customer_input")
public String inputCustomer() {
return "CustomerForm";
}
}
|
使用RequestMapping注解的value属性将URI映射到方法。在上面的例子中,我们将customer_input映射到inputCustomer方法。这样,可以使用如下URL访问inputCustomer方法:
1
| http://domain/context/customer_input
|
由于value属性是RequestMapping注解的默认属性,因此,若只有唯一的属性,则可以省略属性名称。换句话说,如下两个标注含义相同:
1
2
| @RequestMapping(value = "/customer_input")
@RequestMapping("/customer_input")
|
但如果@RequestMapping有超过一个属性时,就必须写入value属性名称。
请求映射的值可以是一个空字符串,此时该方法被映射到以下网址:
RequestMapping除了具有value属性外,还有其他属性。例如,method属性用来指示该方法仅处理哪些HTTP方法。
例如,仅在使用HTTP POST或PUT方法时,才调用下面的ProcessOrder方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| ...
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
...
@RequestMapping(value="/order_process",
method={RequestMethod.POST, RequestMethod.PUT})
public String processOrder() {
return "OrderForm";
}
|
若method属性只有一个HTTP方法值,则无需花括号。例如:
1
| @RequestMapping(value="/order_process", method=RequestMethod.POST)
|
如果没有指定method属性值,则请求处理方法可以处理任意HTTP方法。
此外,RequestMapping注解类型也可以用来注解一个控制器类,如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
...
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/customer")
public class CustomerController {
...
}
|
在这种情况下,所有的方法都将映射为相对于类级别的请求。例如下面的 deleteCustomer方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| ...
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
...
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/customer")
public class CustomerController {
@RequestMapping(value="/delete",
method={RequestMethod.POST, RequestMethod.PUT})
public String deleteCustomer() {
return ...;
}
|
由于控制器类的映射使用“/customer”,而deleteCustomer方法映射为“/delete”,则如下URL会映射到该方法上:
1
| http://domain/context/customer/delete
|